Equinix Network Edge works with Equinix Fabric to provide a virtual cloud on-ramp that can be spun up in minutes to enable inter-network connectivity for a variety of applications. For disparate networks that need to be joined, you can create a single security control point to enforce an inter-network security boundary. Enterprises find this useful for mergers and acquisitions.
Architecture
The topology shown below depicts two disparate networks that must be interconnected as part of an acquisition. The immediate need is to deploy an agile solution that can create interconnectivity between the networks to allow for further integration.
This solution reduces the number of deployed devices and creates a single security control point between the networks. You can also deploy this at distributed control points for inter-region connectivity if needed for performance or regulatory requirements.
Communication between the networks is provided by direct private Layer 2 interconnections over the Equinix Fabric, with the Network Edge device providing Layer 3 routing and security services. The Network Edge device is a virtual network function (VNF) that is hosted by the Network Edge network function virtualization (NFV) platform.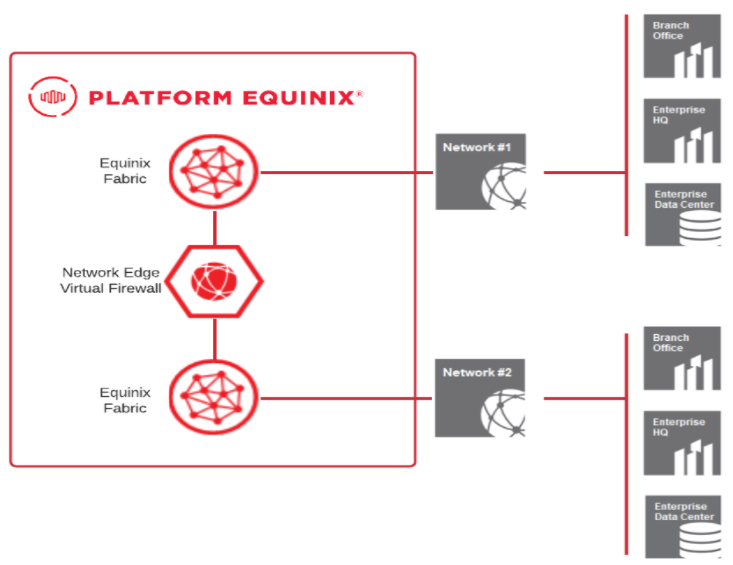
Equinix Components
-
Equinix Fabric – Equinix Fabric is a switching platform that provides private connectivity to a wide selection of providers that are participants on the Fabric. Virtual circuits are provisioned on the Fabric using software-defined networking to establish connectivity to providers that are connected to the Fabric. Virtual connections can be created using the Fabric Portal or APIs.
-
Equinix Network Edge – Network Edge is an ETSI-compliant NFV platform that hosts VNFs (routers, firewalls, and SD-WAN) from various vendors such as Cisco, Juniper, Palo Alto, Fortinet, Versa, Aruba, and Check Point. VNFs can be deployed in real-time and, once deployed, you can start building virtual connections to providers on the Fabric.
Network Connectivity
-
Enterprise Networks – Network 1 and Network 2 are the two networks that must be interconnected after the acquisition.
-
Network Service Providers (NSPs) – NSPs provide the network connectivity to ingress the Equinix Fabric. Any provider that is on the Fabric can be used for Network Edge connectivity.
-
Bring Your Own Connection (BYOC) – Network Edge can only connect to Fabric participants. For participants that are not on the Fabric, customers can use the BYOC feature that allows any network provider to be brought to the Fabric. See the Additional Information section below for more details.
-
Equinix Fabric – The Equinix Fabric serves as the backbone for interconnecting Network 1 and Network 2. The Equinix Fabric is used for quickly building virtual circuits between the networks, and can dynamically adjust bandwidth based on requirements as the integration progresses.
Recommendations
These recommendations provide a starting point. Customer requirements might differ from this list.
-
Choice of location – This architecture example shows connections between the same region. Depending on the region for deployment, latency will vary, which is an important consideration when designing applications with stringent latency requirements. However, some applications might require inter-region connectivity. In those cases, use the global reach of Equinix Fabric to create those connections.
-
High Availability – This architecture shows a single-threaded deployment with no fault-tolerance. Equinix recommends that customers deploy the level of fault -tolerance needed for their business requirements. Network Edge can be deployed with redundant devices or, in the case of some vendors, devices be deployed as a high-availability pair.
-
Network addressing – Connecting disparate networks usually requires some network address translation (NAT) configurations. If needed, Equinix can provide public address space for NAT in each region.
Considerations
When implementing this architecture, consider the following factors.
Performance
In addition to latency, bandwidth between the components and device throughput must is important. The virtual circuits must be sized appropriately, and the devices must support the desired throughput.
Security
Private interconnections on the Fabric to the cloud provider are not encrypted. An application that requires encryption must encrypt either at the application layer, or at the network layer where IPSEC tunnels can be built between the Network Edge device and a cloud gateway. IPSEC tunnels involve overhead, which also affects the device selection.
Equinix Costs
-
Device instance – The cost for the virtual device (does not include the license cost).
-
License for the virtual device – Customers can purchase a subscription license for some vendors. Bring Your Own License (BYOL) is available for all vendors.
-
Virtual circuits – Monthly recurring charges are based on the size of the circuits. Connections between metros across the Equinix Fabric, incur an additional surcharge for the remote connection.
Network Service Provider Costs
Any charge incurred by the NSP will be billed directly from the cloud service provider (CSP).
By deploying a virtual security device on Network Edge, customers can interconnect networks at a single security control point or several distributed control points, while maximizing application performance and enhancing security.

