EBC Single Tenant
An EBC Single Tenant (ST) environment is set up for use by a single user (single tenant). The single-tenant infrastructure consists of dedicated compute units with shared storage and network resources. These resources can be configured and managed via a portal. EBC ST is delivered in a cluster that comprises at least three hosts where compute resources can be efficiently used.
EBC Single Tenant Compute
EBC ST Host
The host in an EBC Single Tenant (ST) environment is based on a standard server configuration. Server Type “EBC HV GC” is the standard server. For EBC environments with more demanding memory requirements, there is a High Memory Hypervisor server type. This can be used on request. The table below lists the currently available hypervisor server types with the amount of usable capacity that a single hypervisor server adds to a cluster.
| Hypervisor Server Type | Deployment | Use Case | # Available GB RAM¹ | # Available CPU Cores¹ | CPU Core Speed |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EBC HV GC v1/v3 | Standard | Generic Compute | 500 | 30 | ≥ 2.4 GHz |
| EBC HV HM v1/v3 | Optional | High Memory | 1000 | 30 | ≥ 2.4 GHz |
Note: Net Capacity of the cluster.
EBC ST Cluster
An EBC3.0 ST environment is delivered in a cluster. A cluster consists of three or more hypervisors of the same type. The type of cluster defines the availability and SLA characteristics of the service. Supported cluster types are:
- Single cluster, single data center
- Multi cluster, multi datacenter
- Single cluster, dual data center (stretched-cluster)
A single cluster, single data center is advised for applications that demand high availability. The recovery ability for this cluster type is primarily realized by the backup. If your application demands the highest availability and ability to recover, the stretched cluster and multi cluster multi data center are advised. The stretched cluster option is used if the application availability depends on the infrastructure, due to synchronous replication (RPO=0). VMs in this case, can be recovered in the second data center in minutes without data loss.
The multi cluster, multi data center type is advised if the application itself can manage the availability and ability to recover. An EBC ST environment has a cluster configuration of at least three hosts in which two hosts are for use and one is spare (N + 1 principle). The (N + 1) cluster has a maximum of 15 hosts (14 + 1); an extra spare server is required above this number.
The maximum cluster size is 44 hypervisor servers (42 + 2). The capacity of the spare server(s) is dedicated to ensuring high-availability and it's unavailable for regular use and, therefore, it's not included in the net capacity. The overview below shows examples of cluster sizes, including the minimum and maximum sizes, and the associated usable net capacity in numbers of usable CPU Cores and GB RAM.
| EBC ST Cluster Size | Hypervisor Server Model | # Spare Servers | # Available CPU Cores¹ | # Available GB RAM¹ |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3 (2+1) minimum | EBC HV GC v3 | 1 | 60 | 1000 |
| EBC HV HM v3 | 1 | 60 | 2000 | |
| 15 (14+1) | EBC HV GC v3 | 1 | 420 | 7000 |
| EBC HV HM v3 | 1 | 420 | 14000 | |
| 17 (15+2) | EBC HV GC v3 | 2 | 450 | 7500 |
| EBC HV HM v3 | 2 | 450 | 15000 | |
| 44 (42+2) maximum | EBC HV GC v3 | 2 | 1260 | 22000 |
| EBC HV HM v3 | 2 | 1260 | 44000 |
Note: Net Capacity of the cluster.
An EBC ST environment can include multiple “Virtual Data Centers” (VDCs). For more information about a VDC, see Virtual Data Center. Use cases for multiple VDCs can consist of applying desktop virtualization, separate production and OTA environments, license restrictions or vCPU guarantees. The VDCs use the capacity that the hypervisor servers add to a cluster.
Types of EBC ST Purchase Units
-
Cluster Management is the fee for the management of the cluster.
-
Cluster Hosts are the compute hosts in the cluster, available in the following variants:
- Small Cluster Host – consisting of a minimum of 3 (2 + 1) hosts
- Rack Cluster Host – consisting of a minimum of 24 (22 + 2) hosts
Note: The cluster hosts are committed for the full contracting period.
-
Additional Hosts can be contracted to accommodate growth and contraction in the contract. These hosts can be traded in after 12 months of usage.
Note: Additional Hosts and Cluster Hosts must be of the same type (Generic Compute or High Memory).
-
VMware License Points are a pay-as-you-go item for the billing of the used VMware licenses. VMware licenses are based on the used GBRam for VMs per hour. Only the VMs that are powered-on will be charged.
| Purchase Unit | Type Host | Guarantee | Billing Type | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| EBC ST – cluster management | N/A | * Standard * High * Full | Baseline | Management fee for the cluster. |
| EBC ST Small Cluster Host | * Generic Compute * High Memory | Small Cluster | Baseline | Agreed amount of hosts in the cluster * Small (min 2+1) |
| EBC ST Rack Cluster Host | * Generic Compute * High Memory | Rack Cluster | Baseline | Agreed amount of hosts in the cluster * Rack (min 2+1) |
| EBC ST - Additional Host | * Generic Compute * High Memory | N/A | Baseline | Additional host with 12 month commitment. |
| VMware license points | N/A | N/A | Pay as you go | VMware licensing fee |
EBC vCPU
On the EBC platform, one CPU is equal to at least 2.4 GHz. There are three vCPU variants, each with its own guarantee value. The standard variant guarantees 25% of the capacity (0.6 GHz); called the guarantee value. The guarantee value on vCPU resources in the standard variant then is 1:4. The available vCPU guarantee values are shown in the below table.
| vCPU Variant | vCPU Guarantee Value | Use Case |
|---|---|---|
| EBC vCPU Standard Guarantee (default) | 1:4 (25%) | * Generic production servers * OTA servers |
| EBC vCPU High Guarantee | 1:2 (50%) | * Medium load application servers |
| EBC vCPU Full Guarantee | 1:1 (100%) | * Terminal servers * High-load application servers * Latency-sensitive application servers |
Using EBC ST
- You can choose multiple hosts and clusters that match the resource request.
- Multiple guarantees of vCPU can be mixed in one EBC ST Cluster by adding an extra Virtual Data Center (VDC).
- EBC ST has, within the limits of the host, no maximum size of a VM for the use of compute resources. There are recommendations for the best performance of a VM. Adding more compute resources to a VM above the recommended size does not always lead to performance improvements.
- For EBC ST, the maximum recommended VM size is 8 vCPU and 64 GB vRAM.
EBC Single Tenant Storage
Storage is a fixed part of the EBC platform and it's available in a variety of storage policies representing different performance levels (tiers). Each disk assigned to a VM is linked to the desired policy at creation and in this way gets the desired performance level. Here is an overview of the storage policies.
| Storage Policy | Tier | Use | RPO=0 Replication | IOPS / GB | Max. Performance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ultra performance | 0 | Enterprise DB (Logs), AI, Machine Learning | No | 15 | 15000 IOPS |
| High performance | 1 | DB (Logs), RDS/SBC, VDI Low latency beneficial workloads | Yes | 9 | 8000 IOPS |
| Performance (default) | 2 | Generic VM’s, App / Web services, High performance File services / Object storage | Yes | 4 | 2000 IOPS |
| Standard | 3 | Back-up, Generic File services / Object storage | — | 1 | 500 IOPS |
Note: Maximum value of IOPS at 65% read / 35% write with 8 KB block size.
RPO=0 Replication
An option for EBC storage is that the data from one site is continuously replicated to a second location. This option is suitable where an RPO value of 0 (zero) is required. Every write to the data is immediately performed on both sites. Only when the data is written correctly on both sites, a commit takes place. In the event that the storage on site A is unavailable, the storage on site B is accessed.
File Storage Premium is only available for the High Performance and Performance Tiers. In combination with EBC ST Premium, an infrastructure can be delivered with RPO=0, and an RTO of 1 hour. The implementation of EBC storage premium is the Active Passive variant, which means that the primary location is always site AM3, and the secondary location is ZW1. In the event of a disaster, writing and reading can take place in ZW1.
Features that apply to storage policies in EBC Single Tenant Storage
- Minimum recommended virtual disk size is 40 GB
- Maximum virtual disk size is 8 TB
- Performance values are limits per allocated virtual disk to a VM
- Storage capacity is allocated in multiples of 250 GB to a specific storage policy within the VDC
- Storage capacity is allocated per policy in a VDC and is not transferable to additional VDCs
- On reaching the capacity limit (agreed amount + 50% margin) of a storage policy, adjustments that require additional storage cannot be implemented
EBC Single Tenant Storage Purchase Units (PU)
EBC Single Tenant Storage is available in purchase units of 1 GB, 1 TB, >100TB or 1PB per storage policy. On the storage platform, extra capacity is reserved per policy for any additional consumption. The reservation is 50% of the number of purchased units. When ordering more than 10TB, the extra capacity is determined in consultation.
Note: Storage capacity is calculated based on the following assumptions:
- 1GB = 1024MB
- 1TB = 1000GB
- 1PB = 1000TB
The overage storage is charged on the pay-as-you-go basis.
| Purchase Unit | Tier | Calculation Type | Unit | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| EBC Storage | * Ultra performance * High performance * Performance * Standard | Baseline | * 1GB * 1TB * 1PB | Number of PUs as agreed with the customer. |
| Overage | * 1GB | Additional consumption above baseline. |
For the RPO=0 variant, the price includes the storage on two locations, so 1GB RPO=0 includes the 1GB at AM3 and ZW1. A Self Service module is available in Service Now to increase the number of purchase units of your settlement. The increase of the available storage according to the settlement is deployed immediately.
EBC Single Tenant Storage Consumption
To calculate shared storage, the consumption per policy and allocated capacity of all linked virtual disks is measured according to use by:
- VM swap files
- Snapshots
- File in a Library (vApp templates and ISOs)
If you want to link more than 4 TB to one or more VMs, Equinix recommends using the Equinix Managed Storage Service (EMSS). Via the EMSS, storage can be linked within the client’s VMs without the intervention of the EBC platform. An example is the use of a virtual back-up server. Advantages may be that the EBC VM back-up does not disrupt its own back-up cycle and data is not unnecessarily duplicated. Optional snapshots or extra copies of the data stored within the EMSS service can be made available in a second site.
EBC Single Tenant Network
The EBC platform offers various virtual network functionalities that can be configured in the EBC portal, next to that connectivity to internet and/or WAN connections are offered in a single and multi-site mode by using Edge.
Edge Gateway
The network interface between the Virtual Data Center (VDC) and external networks such as Internet and WAN has various configuration options, the exact choice depends on the desired functionality. The following options are available:
- Edge gateway shared internet
- Edge gateway single
- Edge gateway stretched
The configuration of the edges also defines the network options between multiple VDCs, e.g. distributed firewalling, and inter-site networking.
Edge Gateway Shared Internet
When only using internet as a connectivity option with a maximum of five IP addresses per VDC, the Edge Gateway Shared Internet will be sufficient. The related Internet product is ECforMS and must be purchased separately. When an IP block of eight or more IP addresses is needed, select Equinix Internet Access for the internet connection product. On the Edge Gateway Shared Internet, only ECforMS can be configured. Other options like WAN connectivity to colocation or Public Cloud is not available with this Edge option. When in a later stage WAN connectivity or a larger IP blocks are needed, an IP renumbering and migration to another edge type is necessary.
Edge Gateway Single
This option is best suited when a VDC has connectivity via Equinix Internet Access for the internet and/or connectivity to a second VDC, cabinet, cloud provider or on-premise location. The Edge gateway is available in two configuration options:
- Shared – This option offers the feature to connect multiple routers to the same internet or WAN connection using NAT.
- Dedicated – A single Edge gateway connects the EBC networks to the internet and WAN without requiring NAT.
When route advertisement is needed where networks in the VDC are automatically available from the WAN connection, the option Dedicated is necessary. This maybe desirable, for example, if IP-space in the Public Cloud needs to be connected to the same IP-space in the VDC. In all other cases the Shared option is suitable.
Edge Gateway Stretched
This option is available to share networks between data centers in one VDC. There is one router available for the internet and/or WAN connectivity. This option supports the use of route advertisement so networks in the VDC are available from the WAN connectivity. This option is obligatory in two scenarios:
- EBC ST Premium where hosts are in two data centers in a stretched cluster configuration.
- In a disaster recovery scenario with two VDCs and EBC Availability.
Additional Edge Gateway
This option enables adding an Edge Gateway to an existing Edge Gateway Single instance (applicable to Shared type Edge Gateway instances). In this scenario, multiple routers can be connected to the same Internet or WAN connection. For example, when using multiple VDCs for Production, test and development.
Internal Networks and VDC Groups
As part of the EBC service, 250 internal L2 networks per VDC are included in the service. You can create these networks through the self-service functionality. If multiple VDCs are used and the internal networks need to be available in all VDCs, a VDC-Group is needed. Internal networks within the same Equinix data center can be created via self-service. Internal networks can also be isolated for example for a backend network. If VDCs are needed in multiple data centers, VDC-group can be requested with a service request. Inter-site networks can be created in self-service. Afterwards the Networks are charged per network.
EBC Flex Network Purchase Units Charges
| Purchase Unit | Type | Ordering and Billing |
|---|---|---|
| NSX License | * Advanced * Enterprise * Enterprise Plus | The NSX license is charged per GB vRAM of the VMs where an NSX function is used. It is a Pay per Use item and charged based of the usage in the past month. |
| EBC Edge Gateway Shared Internet | The Internet Edge Gateway is charged per instance and ordered in advance. | |
| EBC Edge Gateway | * Single * Stretched | The Edge Gateway is charged per edge. Edges are ordered in advance and cannot be ordered via the self-service option. |
| EBC Additional Edge Gateway | Additional Edge Gateways are charged per edge, they can be created via a service request. | |
| EBC inter-site networking | NSX Multisite network is charged as a pay per use item per network the networks can be created in the portal |
The purchase unit for NSX licenses per type applies to the Virtual Network Feature levels of Advanced, Enterprise and Enterprise Plus you can find the table with the NSX features per Edge Gateway below. When using a Dedicated routing instance in the Single or Stretched variant, all VMs with networks connected to the Edge Gateway will be charged for NSX Advanced Licensing. Within the VDC you can set up VMs and network services at your discretion.
| Edge Gateway Type | Selv-service Feature Description | NSX Feature Level |
|---|---|---|
| None | Advanced Firewall (Policy-based security zones through micro-segmentation) | Advanced |
| Virtual L2 networks | None | |
| Edge Gateway Shared Internet | Standard firewall | None |
| Advanced Firewall (Policy-based security zones through micro-segmentation) | Advanced | |
| Routing, IPv4 | None | |
| NAT | None | |
| DHCP | None | |
| VPN (layer 2) | Advanced | |
| VPN IPSec layer 3 Site to site “tunnel” based | None | |
| Edge Gateway Single/Stretched | Standard firewall | None |
| Advanced Firewall (Policy-based security zones through micro-segmentation) | Advanced | |
| Routing, IPv4 static and dynamic(BGP) | None | |
| Routing, IPv6 static | None | |
| Routing, IPv6, dynamic(BGP) | Enterprise | |
| NAT | None | |
| DHCP | None | |
| VPN (layer 2) | Advanced | |
| VPN IPSec layer 3 Site to site “tunnel” based | None | |
| Route Advertisement (VRF) | Advanced | |
| Multi-site network | Enterprise |
Own Routers
If your organization prefers to use its own router or firewall solutions, you may consider using the Basic feature level. The NFV self-service features that require the virtual routers are not available for this level, avoiding charges. Because external routers introduce complexity to the solution a fee is required for the support.
| Purchase Unit | Type | Ordering and Billing |
|---|---|---|
| External Router Support | each | Preordered, monthly fixed fee. |
External Networks
External networks are an optional part of the EBC service up to a maximum of 25 per VDC. EBC External network is used to extend L2 networks (VLANs) outside of a VDC in single or multiple data centers. Examples include connections to a cabinet or carrier, and to:
- Equinix Managed Storage - File
- Equinix Application Platform (Kubernetes container platform)
- Equinix Fabric
- Equinix Connect
VLANs connected via external networks are made available within EBC, and can be translated by Equinix to avoid overlap between other EBC tenants.
Note: Unlike internal networks, external networks cannot be created through self-service, and must be requested through a service request. Multisite external networks are available on special request only. Maximum bandwidth capacity per external network is up to 5 Gbps.
| Purchase Unit | Type | Ordering and Billing |
|---|---|---|
| External Network | each | Preordered, monthly fixed fee. |
Infrastructure Port
To connect to a cabinet, carrier, Equinix Fabric, or in some cases a VDC in a remote data center, an Infrastructure Port is required. This is only offered in a redundant configuration, consists of switch ports configured in a redundant way, and includes the cross-connect. Both ports should be of the same bandwidth, with a choice between 1 Gbps and 10 Gbps. In combination with other Equinix services, Infrastructure Port is the basis for Hybrid-Cloud solutions.
The EBC platform offers various virtual network functionalities that you can configure through self-service on five Network Functions Virtualization (NFV) feature levels. Here is an overview of these individual features.
| NFV Feature Level VDC | Self-Service Feature Description | Equinix Virtual Routers Required | Costs Per VM¹ |
|---|---|---|---|
| Basic (Minimal NFV self-service) | * Virtual L2 networks | N | N |
| Standard (Recommended) | * Standard firewall * Routing (static, BGP) * NAT * DHCP * Load Balancing * VPN IPSec layer 3 | Y² | N |
| Advanced | * Advanced Firewall (Policy-based security zones through micro-segmentation) * VPN (layer 2) | N | |
| Enterprise | * IPv6 | N/A | Y |
| Enterprise Plus | * Future functionality | Y | Y |
| NFV Feature Level vAPP | Self-Service Feature Description | Equinix Virtual Routers Required | Costs Per VM |
|---|---|---|---|
| vApp (serving intervApp network traffic) | * Standard firewall * Routing (static) * NAT * DHCP | Y³ | N |
Note:
- For VMs that use NFV features, a surcharge applies, calculated on the number of GB vRAM in those VMs.
- In the minimum configuration, 2 virtual routers in the size “Large” are created per VDC.
- For each Inter vApp network, 1 virtual router in the size “Compact” is created.
The virtual routers supplied by Equinix contain NFV functionalities for all VMs within the VDC.
Virtual Routers
To enable the full set of NFV functionalities in your VDC, Equinix delivers your VDC in the “Standard” NFV feature level by default. This requires the virtual routers supplied by Equinix in at least the size “Large.” The virtual routers are available in four performance levels and offer NFV self-service functionalities for your VDC. These virtual routers manage internal and external traffic flows for your EBC environment. With these NFV functionalities, the desired security policy for the organization can be implemented at network level.
Virtual routers can be scaled up and down. The functionalities offered by the various Equinix virtual routers are as follows:
- Compact – Basic performance, automatically created for Inter vApp firewalls and routing
- Large – Standard performance for firewalls, routing, VPN and Load Balancing
- Extra Large – Medium performance Load Balancing and high performance firewalls, routing and VPN
- Quad Large – High performance Load Balancing
EBC Single Tenant Network Purchase Units
EBC Single Tenant Network consists of two purchase units: NSX licenses per type in GB vRAM and the Virtual Router per type. The purchase unit for NSX licenses per type per GB vRAM applies to the Virtual Network feature levels of Advanced, Enterprise and Enterprise Plus. Licenses are calculated on the amount of GB VRAM of the virtual machines that use the virtual network functions. A Virtual Router is also used for the feature levels of Advanced and Enterprise Plus. The purchase unit of a Virtual Router is the number of Virtual Routers deployed per type.
Here's a calculation example of EBC Single Tenant Network: You have opted for feature level Advanced in the VDC. You use the Virtual Network functions for 4 VMs. These 4 VMs have 20 GB vRAM in use. The Virtual Router is of the Large type. In this case, 20 GB vRAM is charged for the NSX licenses Advanced, in addition to the Virtual Router Large.
Network Services Consumption
The consumption of network services within EBC is charged as follows:
| Purchase Unit | Type | Billing |
|---|---|---|
| NSX License | * Advanced * Enterprise * Enterprise Plus | The NSX license is charged per GB vRAM of the VMs where an NSX function is used |
| NSX Virtual Router | * Compact * Large * Extra Large * Quad Large | The Virtual Router is charged per router, Routers are ordered in advance and cannot be ordered via the self-service option. |
Within the VDC you can set up VMs and network services at your discretion.
Own Routers
If your organization prefers to use its own router or firewall solutions, you may consider using the Basic feature level. The NFV self-service features that require the virtual routers are not available for this level, avoiding charges.
Internal Networks
As part of the EBC service, 100 internal L2 networks per VDC are included in the service. You can create these networks through the self-service functionality. You can then share the internal networks between all owned VDCs within the same Equinix data center via self-service. For internal networks between geographically separated data centers, stretched L2 networks can be used.
External Networks
External networks are an optional part of the EBC service up to a maximum of 25 per VDC. EBC External network is used for this purpose to extend L2 networks (VLANs) outside of a VDC. Examples include connections to a cabinet or carrier, and to:
- Equinix Managed Storage (file, block, object)
- Equinix Application Platform (Kubernetes container platform)
- Equinix Fabric
- Equinix Connect
- EBC environment in remote data center
VLANs connected via external networks are made available within EBC, and can be translated by Equinix to avoid overlap between other EBC tenants.
Note: Unlike internal networks, external networks cannot be created through self-service, and must be requested through a service request .
Infrastructure Port
To connect to a cabinet, carrier, Equinix Fabric, or in some cases a VDC in a remote data center, an Infrastructure Port is required. This is only offered in a redundant configuration, consists of switch ports configured in a redundant way, and includes the cross-connect. Both ports should be of the same bandwidth, with a choice between 1Gb and 10Gb. In combination with other Equinix services, Infrastructure Port is the basis for Hybrid-Cloud solutions.
Virtual Routers
To enable the full set of Network Function Virtualization (NFV) features, Equinix typically deploys the VDC in the Standard NFV feature level. The Standard set of features requires the EBC virtual router in at least the size, Large, which is sufficient in most cases.
EBC virtual routers (or, virtual routers) are available in 3 performance levels. Depending on feature and performance needs, the virtual router can be upgraded from Large to a Quad-Large or X-Large size. The Standard NFV feature level provides self-service functionality for your VDC, by managing internal and external traffic flows. Using the NFV features, the desired security policy for your organization can be implemented at network level.
Virtual routers support routing, load balancing, and VPN features in firewall services. A single virtual router supports routing up to 100 internal networks by applying the standard and advanced routing methods. Combined with external networks (for connections to carrier, or Equinix Fabric), a virtual router is capable of realizing most network configurations.
Standard Routing
With standard routing, up to 8, (internal and / or external) networks can be attached to a single virtual router. Routing takes place within the virtual router itself. External networks can only be connected via the standard routing method.
Advanced Routing
With advanced routing, up to 100 internal networks can be attached to a single network interface of a virtual router and is referred as Distributed Logical Routing (DLR). Because it is a logical router, changes to the routing table (for example, adding / removing an internal network) are automatically configured by the platform. Traffic to and from advanced routed internal networks remain within the hypervisor layer and does not pass the virtual router, which impacts firewalls. Network traffic between standard routed networks always passes the virtual router.
The benefits of advanced (distributed) routed networks are mainly the improved scalability of routed internal networks. Secondly, advanced routed networks have a positive effect on bandwidth and latency. Advanced routing is available in NFV feature level Standard, and up to 8 internal and external networks can be attached to the same virtual router using the standard routing method.
Firewall
The EBC platform supports layer-4 (L4) stateful firewall services in the Standard and Advanced variants.
Standard Firewall
Standard firewalls are supported in the typical way by IP address, IP segment, port, and service, on networks attached to the virtual router. This type of firewall requires the presence of the virtual router. Standard firewalls are supported for standard routed networks. To firewall VM’s connected to advanced routed networks, advanced firewalls are required.
Advaced Firewall
Advanced firewall support on and between standard and advanced routed networks is an important security feature of the EBC platform. This enables the use of micro-segmentation and contributes to the principle of Zero Trust Networking. Advanced firewalls are available starting from NFV feature level Advanced. This type of firewall service is also called Distributed Firewalling (DFW). Micro-segmentation makes it is possible to apply firewall rules based on dynamic groups. Examples are, firewall rules based on VM names, tags, and names of internal networks. It is even applicable to firewall network traffic within a single layer-2 (L2) network. Advanced firewalls are supported on standard and advanced routed networks, internal and external networks, and are independent of the presence of a virtual router. This is because firewalls occur on the virtual network card (vNIC) of a VM, and not on a router interface.
Connectivity Use Cases
These use cases offer an overview of the EBC connectivity options, showing how the EBC platform can connect to various network environments.
Colo/Carrier
For the EBC environment to be connected to a Colo (cabinet) or Carrier, EBC External network and Infrastructure Port are necessary. This way, up to 25 external networks (L2) per VDC can be routed within the local data center, to a remote (Equinix) data center, or an on-premises platform. In many situations, routing (layer-3) functionality is needed. In these cases, Equinix can provide this via:
- EBC Virtual Router
- Managed Firewall
- Managed Router
To avoid having overlapping VLAN numbers between customers, the VLAN number of each external network offered is translated into a VLAN number issued by Equinix. The translated VLAN number is used within EBC and its related services. Here are the Equinix services required for the use cases.
| External Network Options | EBC to Cabinet / Carrier in Same EQX DC |
|---|---|
| Type of connectivity | Dedicated connectivity |
| Included Equinix services | 2x Cross-Connect |
| Additional required Equinix services | ≥ 1x EBC External network 1x Infrastructure Port - redundant |
| Bandwidth | 1 / 10 Gb |
| Remarks | Customer VLANs are likely to be translated |
| External Network Options | EBC to Cabinet / Carrier in Remote EQX DC |
|---|---|
| Type of connectivity | Dedicated connectivity |
| Included Equinix services | 4x Cross-Connect |
| Additional required Equinix services | ≥ 1x EBC External network 1x Dual-diverse Metro Connect1x Infrastructure Port – redundant |
| Bandwidth | 1 / 10 Gb |
| Remarks | Customer VLANs are likely to be translated |
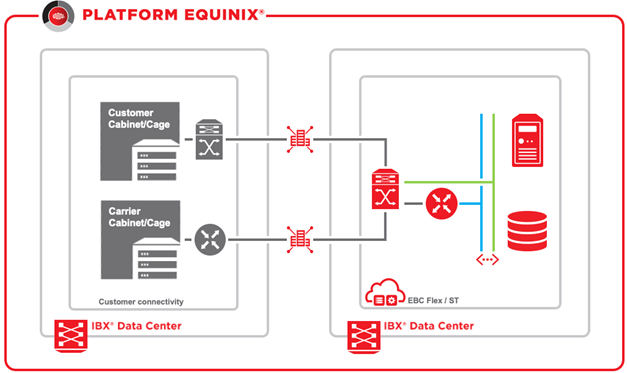
Equinix Fabric
To connect the EBC environment to Equinix Fabric, a combination of services is needed. These include Equinix Fabric ports, EBC External networks, and Infrastructure Ports. Most providers connected to Equinix Fabric require routed (layer-3) based connection. To support Fabric connections to the EBC environment, BGP based routers are required in general. Equinix can provide this type of router via:
- EBC Virtual Router
- Managed Firewall
- Managed Router
Fabric ports can be local or in a different Equinix data center (metro) depending in which Equinix data center the VDC is deployed. If EBC is deployed in AM3, it's local. In ZW1 and EN1, connections are of the type metro, since Fabric equipment is located within the Amsterdam metro area.
Fabric connections are offered in a redundant way. Therefore, 2 Fabric ports (primary and secondary), and 2 virtual connections (one per port) are required. Fabric connections themselves can be of type local or remote, depending where the service provider is located in the Amsterdam region. The following table shows which Equinix services are needed for these use-cases.
| External Network Options | EBC (AM3) to Fabric in Same EQX DC |
|---|---|
| Type of connectivity | Dedicated connectivity |
| Included Equinix services | 2x Cross-Connect |
| Additional required Equinix services | 2x Fabric port≥ 2x EBC External network 1x Infrastructure Port – redundant≥ 2x Fabric Connection (local or remote) |
| Bandwidth | 1 / 10 Gb |
| Remarks | 2 Fabric connections per provider are needed. For each connection one EBC External network is required |
| External Network Options | EBC (ZW1 / EN1) to Fabric in Remote EQX DC |
|---|---|
| Type of connectivity | Dedicated connectivity |
| Included Equinix services | 4x Cross-Connect2x Path-protected Metro-Connect |
| Additional required Equinix services | 2x Fabric metro port≥ 2x EBC External network 1x Infrastructure Port – redundant≥ 2x Fabric Connection (local or remote) |
| Bandwidth | 1 / 10 Gb |
| Remarks | 2 Fabric connections per provider are needed. For each connection one EBC External network is required |
| External Network Options | Dual EBC (AM3 + ZW1 / EN1) to Fabric |
|---|---|
| Type of connectivity | Dedicated verbinding |
| Included Equinix services | 8x Cross-Connect2x Path-protected Metro-Connect |
| Additional required Equinix services | 2x Fabric port2x Fabric metro port1x Dual-diverse Metro-Connect≥ 8x EBC External network 2x Infrastructure Port – redundant≥ 2x Fabric Connection (local or remote) |
| Bandwidth | 1 / 10 Gb |
| Remarks | 2 Fabric connections per provider are needed. For each connection one EBC External network is required. Connections in both DC’s are local redundant. |
Equinix Connect
To directly connect the EBC environment to the Internet, a dedicated connection in the form of an Equinix Connect (EC) may be required. A dedicated EC is advised when requirements include:
- A dedicated link with 1Gb or higher bandwidth
- Anti-DDoS
- Customer provided IP blocks (own ASN supported, not required)
- Equinix supplied IP blocks of /29, /28 or /27
The EC connection is connected to the EBC environment by applying EBC External network and Infrastructure Port. This requires BGP based routers. Equinix can provide this via:
- EBC Virtual Router
- Managed Firewall
- Managed Router
The following Equinix services are needed for these use-cases.
| External Network Options | EBC to EC in Same EQX DCc |
|---|---|
| Type of connectivity | Dedicated verbinding |
| Included Equinix services | 2x Cross-Connect |
| Additional required Equinix services | 1x Equinix Connect port (multi-homed)≥ 2x EBC External network1x Infrastructure Port – redundant |
| Bandwidth | 1 / 10 Gb |
| Remarks | — |
| External Network Options | Dual-Site EBC (AM3 + ZW1 / EN1) to EC |
|---|---|
| Type of connectivity | Dedicated verbinding |
| Included Equinix services | 8x Cross-Connect |
| Additional required Equinix services | 1x Dual-diverse Metro-Connect2x Equinix Connect port (multi-homed)≥ 8x EBC External network2x Infrastructure Port - redundant |
| Bandwidth | 1 / 10 Gb |
| Remarks | Both multi-homed connections are local redundant |
EBC Single–Site
When communication is required within a single EBC location, EBC External network can be used. In this way, layer-2 (L2) communication between EBC Flex, EBC ST, Shared Managed Storage (file, block, object) and Application Platform (Kubernetes container platform) is possible.
| External Network Options | EBC Single – Site |
|---|---|
| Type of connectivity | — |
| Included Equinix services | — |
| Additional required Equinix services | 2x EBC External network |
| Bandwidth | Upto 10 Gb |
| Remarks | Up-to a max. of 25 |
EBC Dual-Site
When EBC services are consumed at 2 locations, Stretched Layer-2 Shared and Stretched Layer-2 Dedicated are available for realizing L-2 connectivity. Both are applicable for EBC and Equinix Managed Solutions products such as Managed Storage (file, block, object) and Application Platform (Kubernetes container platform). The choice between the two is determined by the amount of bandwidth and number of external networks required.
| External Network Options | Stretched Layer-2 Shared | Stretched Layer-2 Dedicated |
|---|---|---|
| Type of connectivity | Shared connectivity | Dedicated connectivity |
| Included Equinix services | 2x EBC External network | 4x Cross-Connect2x EBC External network |
| Required Equinix services | ≥ 1 Stretched Layer-2 Shared | 1x Dual-Diverse Metro-Connect2x Infrastructure Port (primary)2x Infrastructure Port (secondary) |
| Bandwidth | To 100 Mb / 1 Gb | To 1 Gb / 10 Gb |
| Max. # Stretched Layer-2 connections per VDC | 25 | 25 |
Stretched Layer-2 Shared
This is the best choice when less than 10 External Networks are needed between 2 EBC locations, and a maximum bandwidth of 1 Gb is sufficient.
Stretched Layer-2 Dedicated
This option is the best choice if more than 10 External Networks are required, and/or 1 Gb or more bandwidth is needed.
Metering
Equinix Managed Solutions are billed in the following ways:
- Baseline – The contracted quantity of the service (example: purchase unit vCPU, vRAM)
- Overage – The amount of GB consumed above the baseline value (example: the contracted storage baseline is 500 GB, 600 GB are used and the overage consumed is 100 GB)
- Pay per use – Fully variable (example: used amount of GB for back-up)
To measure the quantity of the variable component consumption, Equinix uses metering tools linked to the service management environment. Only the data required to determine the quantity of service consumed are exported to the Equinix billing system. It is mandatory to install the VMware tools on every VM in the EBC Platform.
Reporting
Within the service, the customer can use the vCD portal reporting options to get an insight into its own VDC vCPU, GB vRAM, and storage consumption.
Licensing
For license-related issues, see the Licensing service description.
Demarcation of the Service
- Move virtual disks – It is not possible to move virtual disks between VMs via the EBC web portal and API. For this, create a ticket via the Equinix support desk
- Share virtual disks between VMs – Sharing a virtual disk between multiple VMs is not supported within the EBC. Applying Microsoft Windows Server Failover Clustering (WSFC) with shared disks to EBC is not supported for this reason.
- Physical NIC access from the VM – The application of Single Root I/O Virtualization (SR-IOV) is not supported.
Relations and dependencies
EBC Back-up & Restore
In addition to EBC ST, purchase of EBC Back-up & Restore service is essential. Equinix provides a managed back-up service for EBC. As part of managed back-up, Equinix provides back-up and recovery of only VM-related data.
EBC Migration
EBC Migration provides a migration infrastructure that allows customers to migrate via self-service virtual machines from their own VMware environment to Equinix Business Cloud. After application, a user-specific migration environment is created within the EBC, linked to the user-specific EBC environment. A chosen connectivity is then arranged, based on an internet or direct‑connect connection. A Veeam Back-up & Replication instance must be available at your location. If you are not yet using this software, a standard edition can be installed. On delivery of the environment, you can specify Equinix as your service provider, after which the migration jobs can be created. After a job is created, it can be periodically started. At the start of a job, the replication of data will take place directly in your EBC environment. The replication of the virtual machines is based on VMware snapshots. After all migrations have been completed, you can order the environment to be removed. The migration is settled with a price per environment and a price per virtual machine. More details can be found in the service description EBC Migration.
EBC Connect
An optional part of your EBC environment is access to external network connectivity. The service that makes this possible is called EBC Connect. This service is a necessary component if, for example, you want to connect to your own cabinet, another Equinix data center, an on-premises location, a WAN provider or a combination of thereof. The EBC Connect service is purchased as a redundant connection with a bandwidth of 1 Gb or 10 Gb. EBC Connect must be purchased in combination with other Equinix network services in order to realize a hybrid solution.
Equinix Connect
An optional part of the EBC environment is an internet connection provided by Equinix. Equinix Connect is used in combination with EBC Connect. This combination of services makes a single or multi-site internet connection possible. Based on your requirements, a suitable solution is designed in collaboration with an Equinix Solutions Architect. Ordering options of the Equinix Connect service include provision of Anti-DDoS, bandwidth (including commit), public IP addresses provided by Equinix, and applying your own IP blocks on an Equinix Connect connection. To use the internet connection within your EBC Core platform, equipment is needed to offer BGP-based routing functionalities. Equinix can provide this via:
- EBC Virtual Router
- Managed Firewall
- Managed Router
If you have equipment with BGP-based routing functionalities, you can use that equipment in most cases.
Customer Connect
The Customer Connect service enables you to establish network connectivity between your location and the Equinix data center.
Cross Connect
With Cross Connect, you can connect to another location in the same data center.
Metro Connect
Metro Connect allows you to connect to another EBC location or another Equinix data center.
Equinix Fabric
With Equinix Fabric, you can make a connection to one or more public cloud providers. To establish the connection within your EBC Core platform, equipment for BGP-based routing functionalities is provided by Equinix through those made available by EBC Virtual Router, Managed Firewall or Managed Router. VLANs are applied to make external connectivity available within the virtual data center. They are provided by Equinix as external networks in your VDC.
EBC Internet
EBC Internet is an optional part of the EBC service, with a maximum of five public IP addresses and a maximum internet bandwidth of 1000 Mbps. If the VDC is configured at NFV feature level Standard (see the network functionalities paragraph), the virtual routers supplied by Equinix will handle internet traffic, so that your VDC will be ready for use after delivery. One public IP address is assigned when your VDC is delivered. If you need additional public IP addresses, you can contact the Equinix Support Desk. Additional addresses are not consecutive.
Managed Firewall
An optional part of the EBC environment is a Managed Firewall solution. This service may be relevant to:
- Facilitate secure access to the public cloud and other external networks
- Add functions for intrusion detection (IDS) / intrusions prevention (IPS) to the EBC platform
- Have direct access to the management layer of the EBC platform
- Transfer operational firewall management to Equinix
Important features of the Managed Firewall service are:
- Firewalling
- Routing
- IDS/IPS (order variant)
- Load balancing
- VPN
Managed Router
An optional part of the EBC environment is a Managed Router solution. This service may be relevant to:
- Facilitate access to the public cloud, WAN providers and on-premises networks
- Transfer operational router management to Equinix
Important features of the Managed Router service are:
- Dynamic routing
- Static routing
- NAT
- Virtual Router Redundancy Protocol (VRRP)