Connecting Virtual and Physical Environments
This topic focuses primarily on connecting your virtual device to your Network Service Provider (NSP), a common use case that often involves a physical aspect to the solution.
Connecting customer environments together is as important as connecting to clouds and the Internet for most customers.
As the Equinix Fabric grows, more network service providers and enterprises are joining the platform, offering their products and services. Occasionally, the destinations you need to reach from your virtual device are not present on the Equinix Fabric and an alternative for reaching them is required.
To connect a virtual device to a physical environment, the user needs to access the outside physical world from a device that is deployed on a shared compute node with virtual interfaces. This is usually done with cross connects from one data center or cage space to the next.
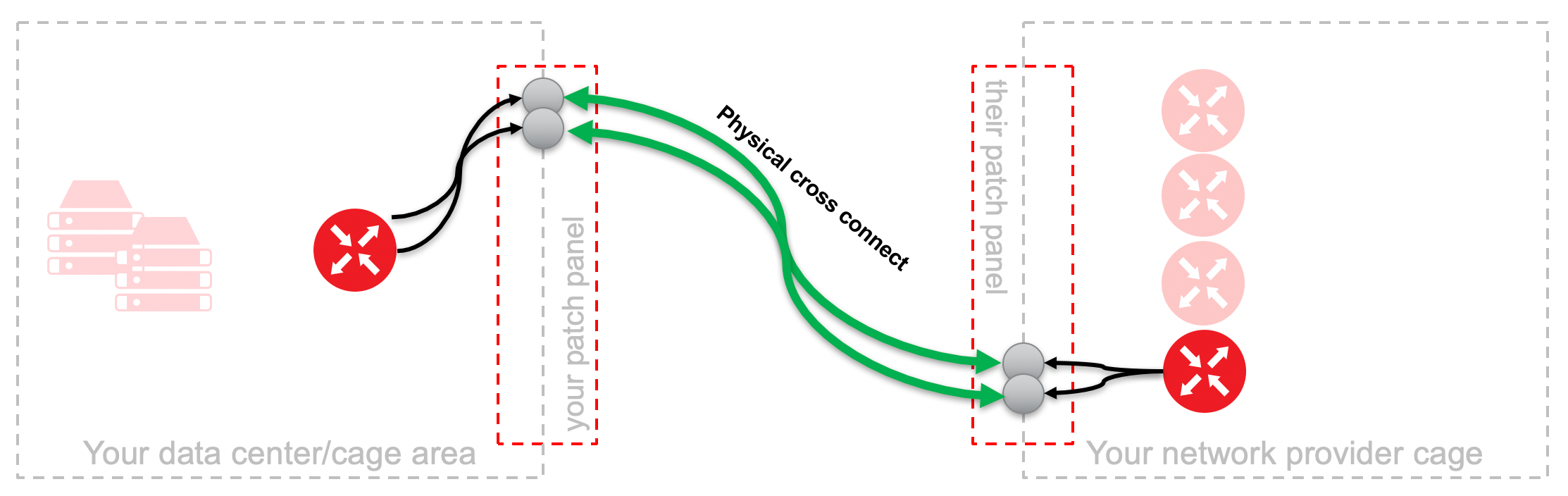
To facilitate this same activity with a virtual device that doesn't occupy a cage, we virtualize certain aspects of the solution, and there are many ways to do so.
All Network Edge devices connect to the outside world through the Equinix Fabric platform or through the internet (Equinix Internet Access), as this satisfies many use cases with no further connection needs. However, many users find that they want their virtual devices connected to an NSP that they want to or are already doing business with. Often this helps normalize the device with the rest of a global network deployment by integrating it with an existing MPLS network.
Connection is facilitated through the Equinix Fabric, and all traffic flowing in and out of the Equinix Fabric does so through a physical port, whether it's dedicated to a single user or service, or it's used in a multi-tenant way.
For a virtual device user to get to a network service that you have procured, there are a few ways this can be done through the Equinix Fabric with BYOC.
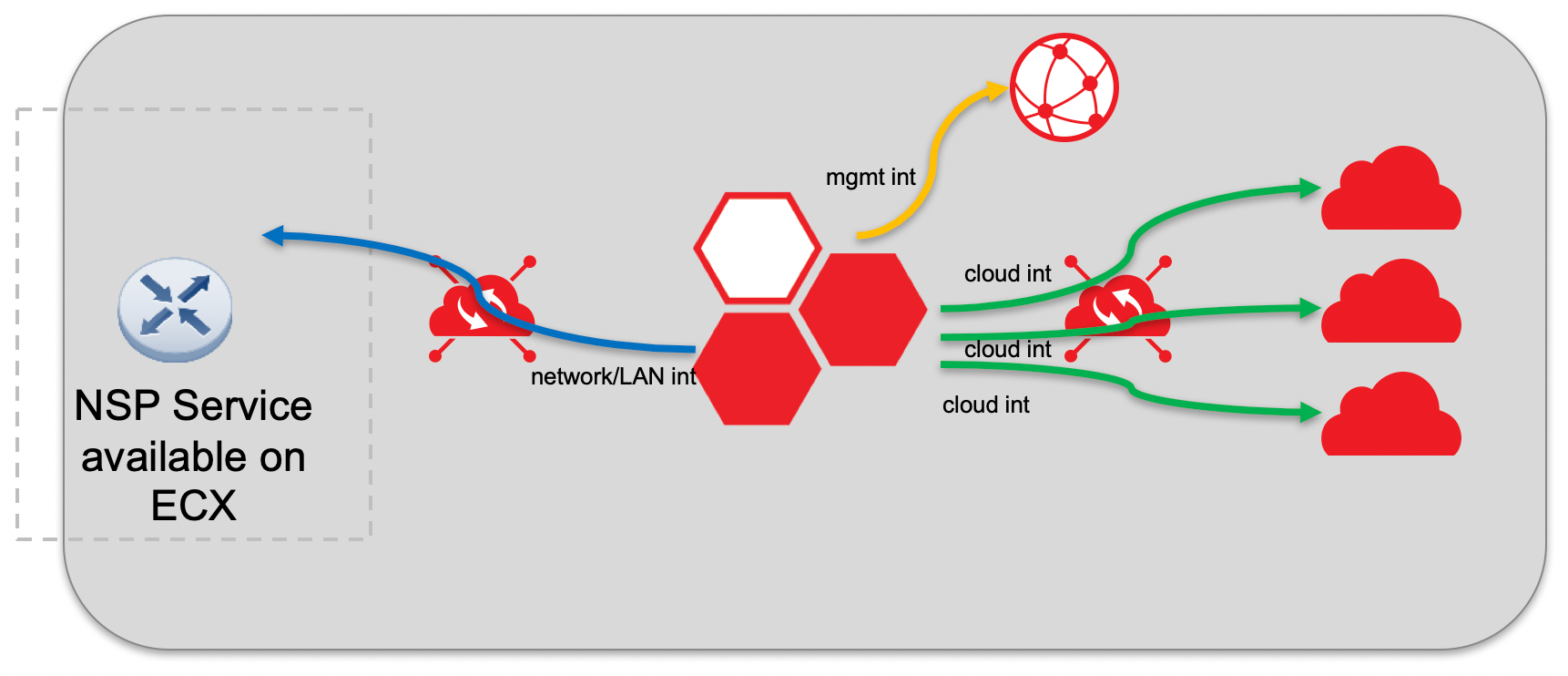
NSP is a Seller on Equinix Fabric
In this scenario, the network provider offers its network products and services publicly through the Equinix Fabric. The virtual device owner creates a connection to the known, published service Equinix Fabric. This is the simplest method for virtual device owners, and we encourage network providers to participate in the Equinix Fabric ecosystem wherever possible.
If the NSP has a presence on the Equinix Fabric, find them in the list of services available and create a connection.
Bring Your Own Network Service
The user purchases connectivity from a network provider in a specific data center, and the NSP terminates that connectivity as a port in an Equinix facility, providing necessary details so that you can order a port and connect to it through Equinix Fabric.
If you'd like to connect to a network provider with a virtual device, but the network provider is not present on Equinix Fabric as a seller, they must be able to do one of the following:
- Have a presence on the Equinix Fabric that they use for buying Equinix Fabric service and be able to use that port as a destination for you to connect to.
- Have a physical presence in Equinix facilities where they can reserve a physical port for you and generate a Letter of Authorization/Customer Facilities Assignment (LOA/CFA). If the NSP uses this method, the virtual device owner should follow this process to get connected to the LOA/CFA:
Create a Port
- Order the remote port online.
- Configure the port.
- Load the LOA.
- Enter the necessary contacts for physical tie-down work.
- Schedule the turn-up call.
Create Service Profile
- Enter basic settings.
- Make profile private and add internal users.
- Load the port you created.
- Specify speeds.
- Obtain operational approval where needed.
Connect to Your Profile
- Create a connection from your device (Connect to Self)
- Select the profile you created.
- Select the appropriate Z-side information (port you create and VLAN provisioned by the NSP).
LOA/CFA
LOA/CFA is permission that the owner of a space in a data center grants to another that allows access to their cage for a certain purpose. The CFA is a specific location in the data center, usually referring to cabinets, shelves, and plugs, where the connection shall occur.
Remote Port
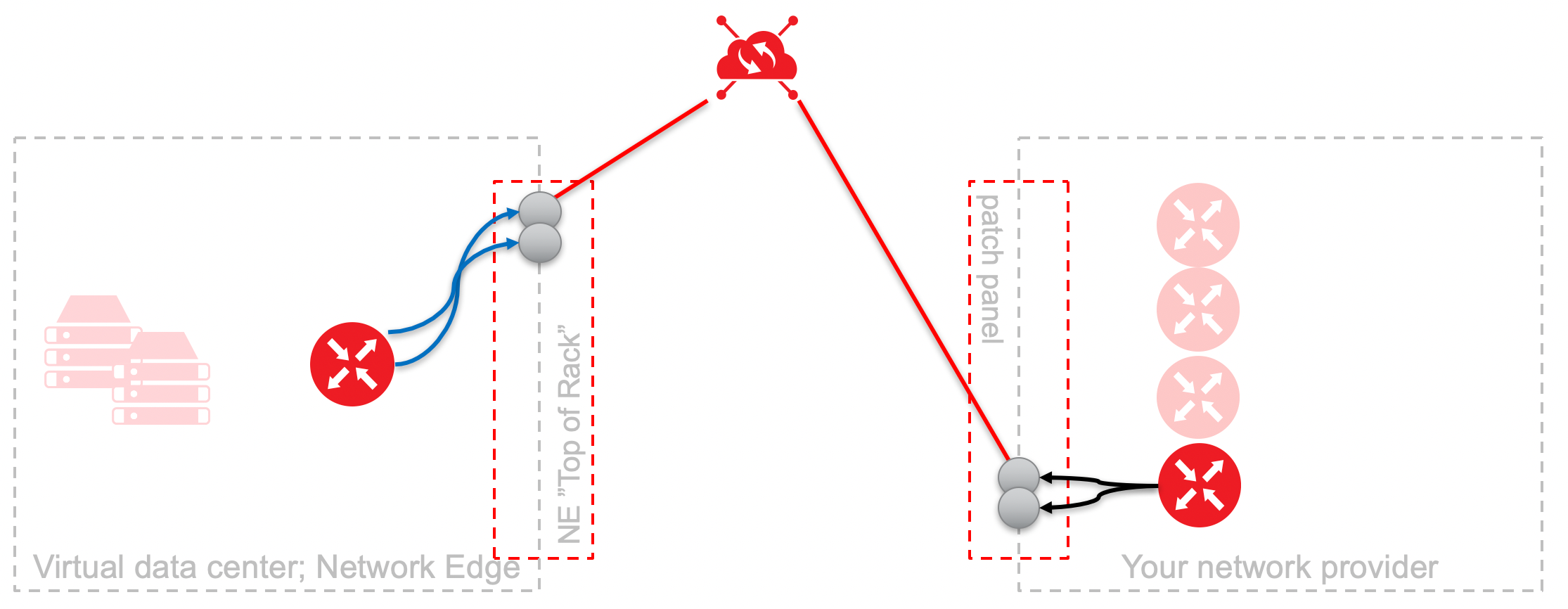
A port is a physical place where interconnection occurs between two parties. The cables from each party are physically plugged together so that data can pass. With a remote port, the port is owned by the customer, but the location is not. The virtual device customer procures a remote port and owns that port in a physical location that the customer has no actual presence in.
A remote port can be used when there is no physical CPE router colocated in an Equinix data center. The virtual router can be connected to the Equinix Fabric switch through a Layer-2 service profile with the NSP connection terminated directly on the Equinix Fabric switch. The service profile is owned by the customer who is responsible for setting the correct attributes to establish connectivity.
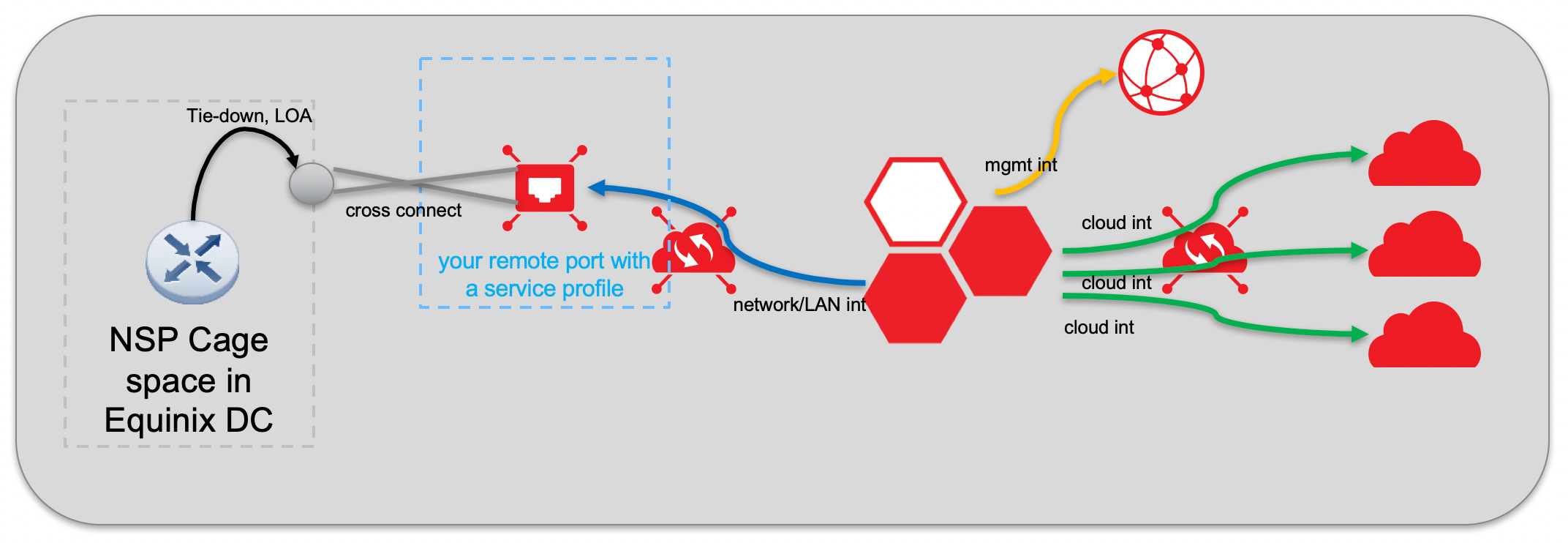
To connect, place an order with your NSP and then provide Equinix with the LOA/CFA giving Equinix the authorization to connect between the NSP demarcation point and the Equinix Fabric switch. As in the case of a physical connection, you can also connect to any location on the Equinix Fabric (local or remote).
Connect To Your Colocated Resources
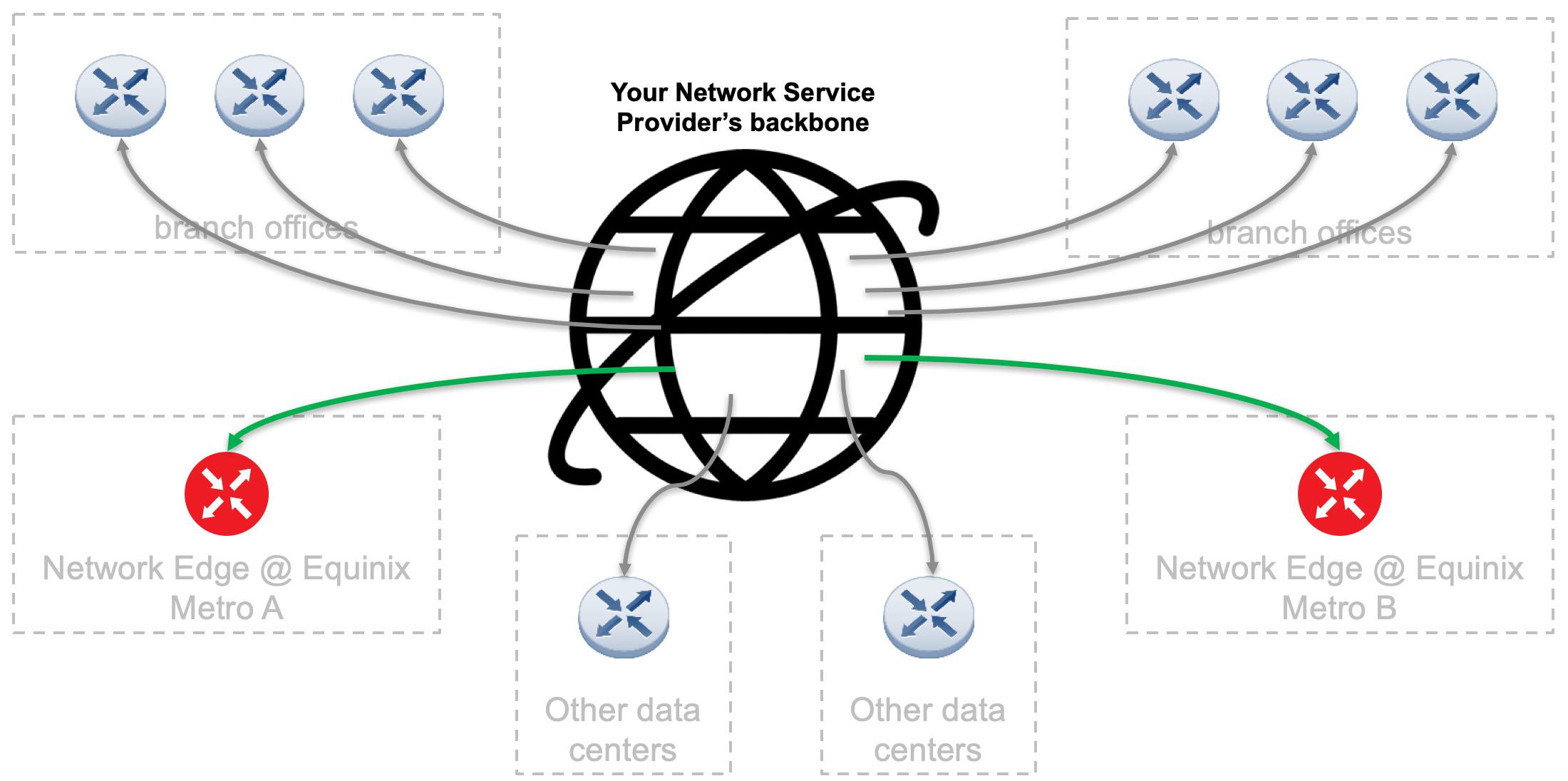
Customer provided equipment can be colocated within an Equinix data center. To reach it, you need a physical port on the cloud exchange and a defined service profile to connect the virtual router. The virtual cross-connect can happen between any two locations on the Equinix Fabric (either local or remote). In the diagram below, the owner of a virtual device has connected remotely to a cage in another metro using the Equinix Fabric as the method for reaching the port.
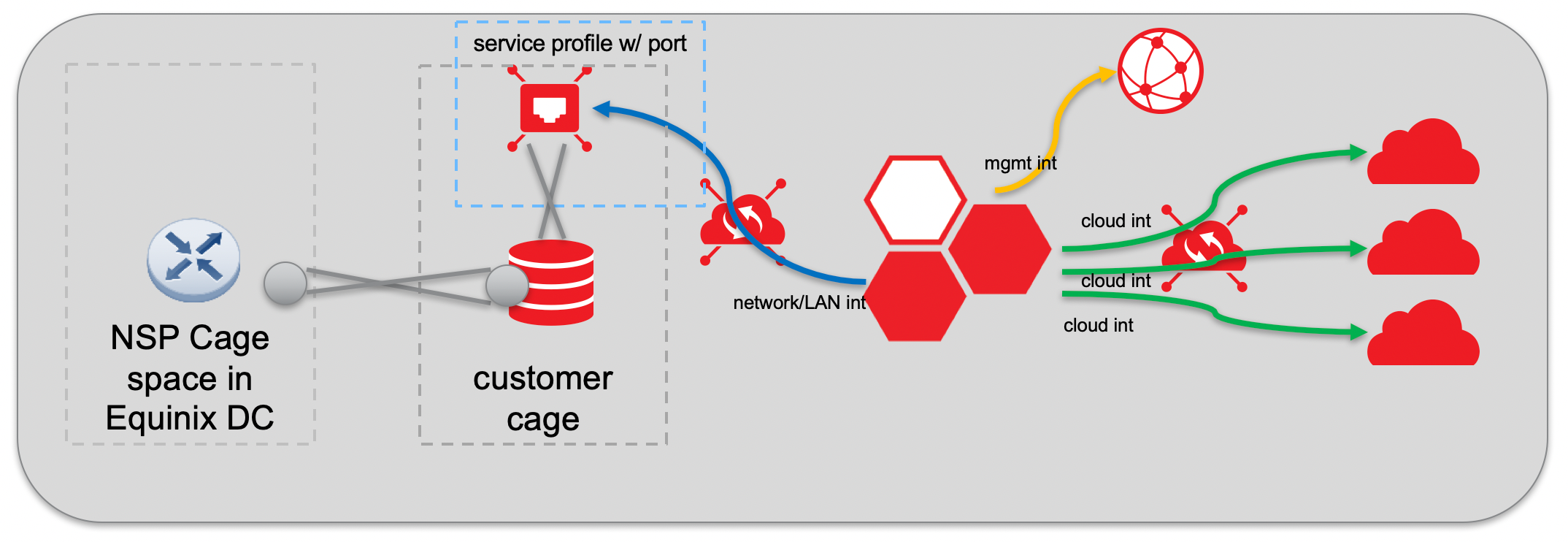
Ultimately, the way we facilitate any connection from virtual to physical, including a network connection from the customer provider, is through the Equinix Fabric.
The reasons for connecting virtual and physical environments include:
- Connecting the virtual device to a LAN or WAN network
- Connecting the device to an existing global NSP that the user is contracted with for MPLS, EVPL, Internet, or other telecommunications services
- Chaining the virtual device to another virtual or physical device or environment off the Equinix platform
- Attaching the device to the edge of other private resources such as deployed servers, storage, or other IT equipment
Basic Steps and Concepts to Connect
In any of the scenarios explained above, the basic connection steps are about the same.
- Order network services
- Buy and configure Equinix Fabric resources
- Connect your device to an NSP
- Customize your device
The implementation of the basic connection steps might differ depending on which method you need.
Order Network Services
The first step is to order services from the network provider. Equinix offers no specific guidance on which providers and products are best. However, when Equinix observes deployments from specific providers and product types that go well, we catalog them in our documentation so customers know which ones work best. If the NSP is part of the Equinix Fabric, there is a good chance that their product inter-operates with your device.
When terminating network services to your virtual device, there might be special configurations needed to ensure they operate properly. The user is responsible for ensuring this is done properly on their device. While Equinix can't predict or specify the exact needs of every NSP and their portfolio of products globally, the services typically include:
- Ethernet type Layer 2 services such as EVPL, E-LAN, or EPL
- Layer 2.5 type services such as MPLS
- True Layer 3 peering services such as IPVPN or DIA/high-speed internet
Each of these network services drive different needs on your device, such as IP addressing, protocol configuration and enablement, VLAN assignment, rate limiting, or others.
Not all traffic types have been tested to work with every virtual device, but the platform is designed to be quite open and flexible. Your NSP’s guidance on configuration is important to the success of the interconnection.
Equinix follows a number of rules when deciding and provisioning network services that increase the likelihood of it being successful:
-
The hand-off from your network provider can be a VLAN-tagged or an untagged service, whether it's already on Equinix Fabric or you want to connect it to Equinix Fabric.
-
The customer needs to know the VLAN assigned to the traffic so it can be configured properly on the Equinix Fabric.
-
The NSP should provide the necessary IP addressing, label switches, VLAN, or other logical inventory needs to fully configure the device and the port.
-
If you terminate a public internet service, the number of routes might be restricted because a full internet routing table could heavily burden the performance of a virtual device. We recommend you either consider physical deployments for route tables beyond 2-5K routes, or deploy with network address translation (NAT).
-
Your NSP service should be policed or rate limited and should never exceed the total size of your virtual device licensed throughput.
Nearly any protocol can be supported if the specification from your virtual device vendor says it's supported, but we can't test every single one. See the Equinix Fabric documentation to discover if there are any limitations to that platform for your traffic type. See the Device Configuration section in the Network Edge documentation for specific vendor limitations.
Buy and Configure Equinix Fabric
To connect through Equinix Fabric, certain things must be present, whether they are owned by the NSP or the customer. To connect from one side to the other, two ports and a connection between them are required. Fortunately, many of these components are already present.
On the virtual device side, each device already comes with a virtual port facing the Equinix Fabric. Therefore, bulk of the work needed is to get to the network service (or the Z-Side):
- If the NSP is an actively selling services on the Equinix Fabric, simply create a connection to that service, so you can jump to the next step.
- If the NSP provides a port on the Equinix Fabric, they need to specify which service to connect to. You can jump to the next step to connect the device, but must first have permission from the NSP to see the service.
- If the NSP provides a physical tie-down location only in an Equinix data center, procure a port to connect the NSP to, and then define a service around that port so that you can connect to it
When you opt to connect to your NSP from a virtual device, we recommend that you use the special connection flows rather than standard create connection flows. This ensures your NSP connection is on a discrete interface and VRF that allows you to configure it separately and differently from other Equinix Fabric cloud traffic. Each virtual device is launched with a reserved network provider interface whether you opt to use it or not.
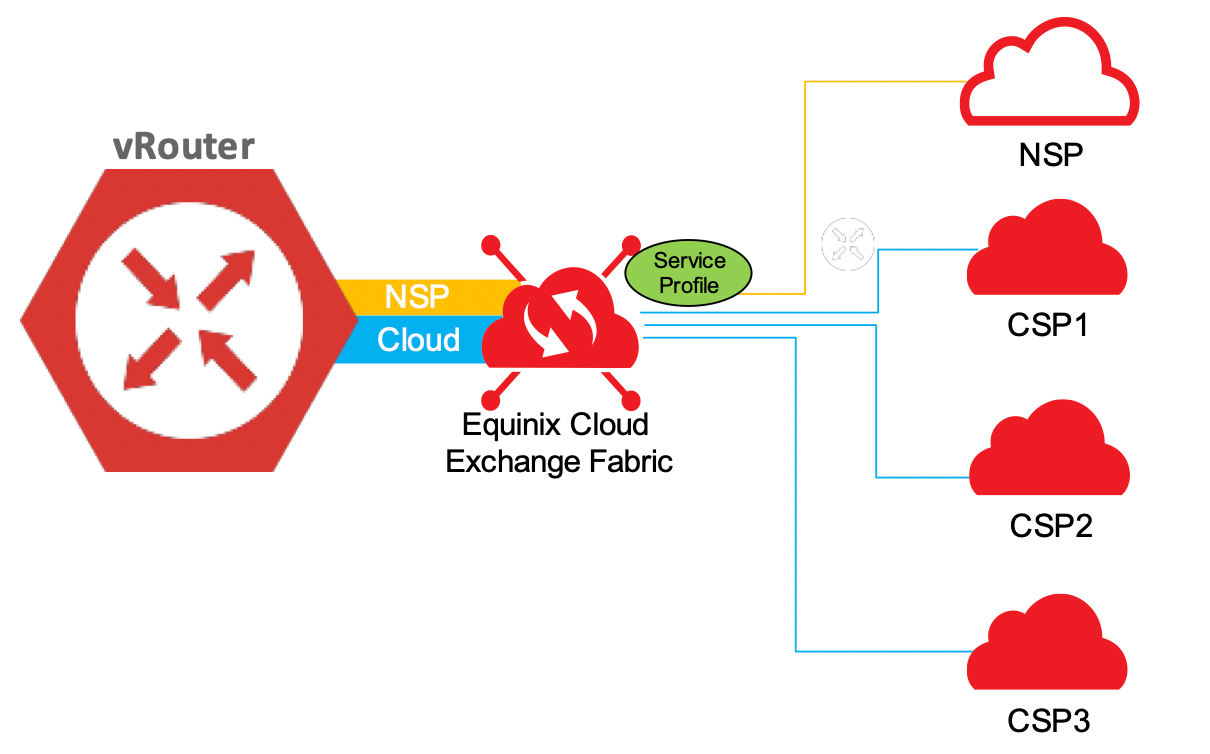
Service Profiles
Connect to anything on the Equinix Fabric as a destination or Z-end by using a service profile. Anyone can create a service profile on Equinix Fabric with a port, and the service profile can be private so that only authorized users can see and use it.
You can delete the profile or remove the port from the profile immediately after creating a connection from your device to the port, and the connection remains in place. Users can also add BGP settings to ensure peering occurs between the environments. For this type of connectivity, Equinix recommends a Layer2 service profile.
Go to the My Company section in the Equinix Fabric documentation for more information about service profiles.